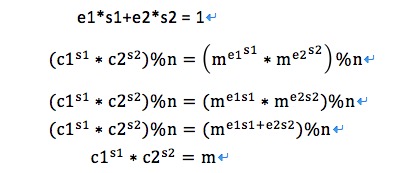1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| import binascii
# q = 167
# p = 173
# m='4F'
n = 28891
(e1,d1,n) = (29,8861,n)
(e2,d2,n) = (23,6207,n)
d = 59
m = int(binascii.b2a_hex("4F"),16)
c1 = pow(m,e1)%n
c2 = pow(m,e2)%n
print "c1=",
print c1
print "c2=",
print c2
def gcd(a, b):
if a == 0:
x, y = 0, 1
return (b, x, y)
tup = gcd(b % a, a)
d = tup[0]
x1 = tup[1]
y1 = tup[2]
x = y1 - (b / a) * x1
y = x1
return (d, x, y)
# solve the Diophantine equation a*x0 + b*y0 = c
def find_any_solution(a, b, c):
tup = gcd(abs(a), abs(b))
g = tup[0]
x0 = tup[1]
y0 = tup[2]
if c % g != 0:
return (False, x0, y0)
x0 *= c / g
y0 *= c / g
if a < 0:
x0 *= -1
if b < 0:
y0 *= -1
return (True, x0, y0)
(x, a1, a2) = find_any_solution(e1, e2, 1)
if a1 < 0:
(x, c1, y) = find_any_solution(c1, n, 1) # get inverse element
a1 = -a1
if a2 < 0:
(x, c2, y) = find_any_solution(c2, n, 1)
a2 = -a2
m = (pow(c1, a1, n) * pow(c2, a2, n)) % n
print "m =",
print m
q = hex(m)
q = q.replace('0x','')
q = q.replace('L','')
print binascii.a2b_hex(q)
|